Geopolitics of the Middle East
Important player
Iran
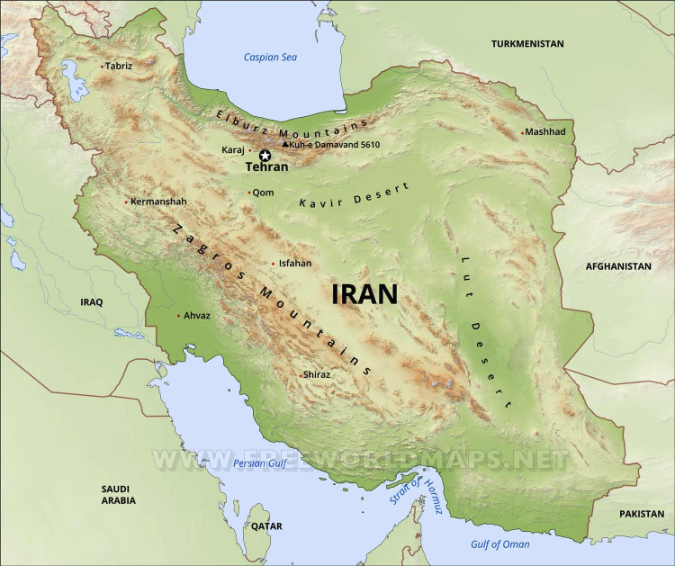
Iran is a very mountainous country, which makes it hard to have an economy with all the different parts connected. There are lots of different minority groups living in Iran, each with its own culture and language. For example, Khuzestan is mostly Arab, and there are also Kurds, Azeri, Turkmen and Georgians. Most people in Iran speak Farsi, which is the language of the Persian majority. Because of this diversity, Iran’s leaders have usually used military force and a powerful security service to keep the country safe. Iran’s leaders know that no one is planning to attack them, but they also know that other countries could use Iran’s minorities to cause trouble and try to change the government.
Potential problem: nuclear weapons threatening other countries
Many countries, especially Israel, are afraid that Iran is trying to build nuclear weapons which could cause a lot of tension in the area. The Israelis are scared because if Iran gets nuclear weapons, other countries in the region like Saudi Arabia might want to get them too. This would mean that Iran would be the biggest and most powerful country in the region. To prevent this, the Saudis might try to buy nuclear weapons from Pakistan. Israel might try to stop this from happening by sending a plane to attack Iran’s nuclear facilities, but this would be very difficult because it is a long way away, and it would also risk angering Iraq and other countries in the area. Another problem is that Iran could close the Strait of Hormuz which could cause problems for the whole world. That’s why so many countries are trying to stop Israel from attacking Iran.
Geopolitical Friends and Enemies
- Friends -Iraq: the US delivered Shia-majority government
- Enemy
- Saudi Arabia: the Summo-dominated government Under the dictatorship of Saddam, the Iraq is a powerful buffer zone between Saudi Arabia and Iran, but now the buffer zone is gone.
- US: they used to fear the encirclement by the Americans from Iraq and Afghanistan, but now the fear is gone.
Turkey
Why EU won’t accept it as a member country
-
Geography
If Turkey is part of Europe, then Europe’s borders would reach to Syria, Iraq and Iran.
Only 5% of the territory of Turkey is considered inside of the Europe. (West of the Bosporus1), the rest are considered in the middle east.
-
Demographic
The disparity in living standard and 75m population. The EU countries are afraid of the influx of labour force from Turkey.
-
Other potential issues
- Human right issues, especially towards the Kurd.
- Religion: the majority of the population is Muslim.
[ ] To what extent did the refusal from the EU result in the reemergence of religious leaders since Mustafa Kemal2?
In the book Prisoner of Geography, the author brought up that continued rejection from the EU, plus the refusal of many Turks to become secularized resulted in Turkish politicians seeking “Plan B”, the alternative to becoming a secularized culturally European country.
There was religious president Turgut Özal3 came to the office and wanted to make Turkey the great land bridge between Europe, Asia and the Middle East, a country that has great power in all three regions. This is also the vision under the current President Recep Tayyip Erdoğan4.
However, it is also the geography of the country that makes the dream hard to be fulfilled.
Relationship with other regional countries
-
With Arab Countries: icy and cooled
Arab countries are generally suspicious of Turkey’s plan to revive the Ottoman’s glory economically.
- Iran: sees Turkey as the most important competitor bother economically and militarily in its backyard. The relationship cooled after the Syrian civil war5, for they are backing opposite sides of the factions.
- Egypt: the Muslim brotherhood policy failed after the second military coup in Egypt, and the relationship between Cairo and Ankara become icy. They even become the major customer of the new energy source created by the alliance between Cyprus, Greece and Israel.
-
Israel: cold war relation
- fill the Turkey and Israel conflict with more details later.
The deterioration of relations between Israel and Turkey after the ascendancy of the Justice and Development Party (AKP). The Israel-Gaza conflict brings a good diplomatic relationship between Turkey and Israel to a halt. 6
Israel, Cyprus, and Greece are working together to get energy from the gas fields near their coasts. Turkey could have gotten energy from Israel, if their relationships are more reconciliatory. However, because of the strained diplomatic relationship, they are still relying on Russia for their energy needs. They are also working with Russia builds pipelines so they can get the energy to other countries in Europe.
-
NATO and US
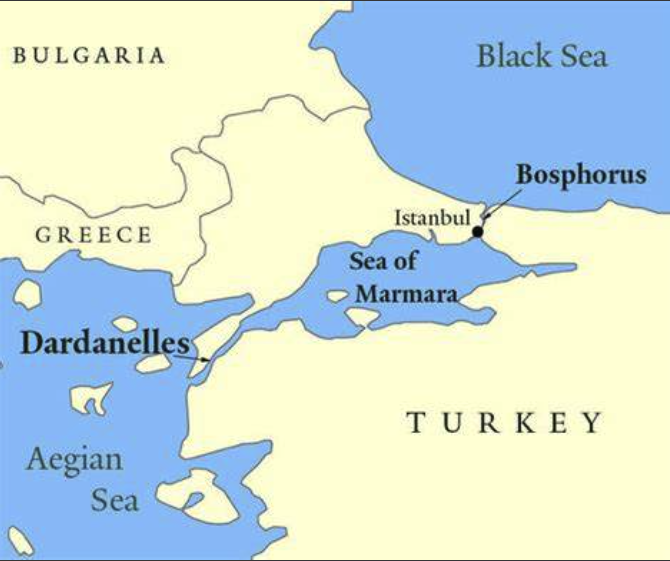
The US wants a better relationship between the Turkey and Israel to strengthen NATO’s position in the eastern Mediterranean. Turkey is a key country to NATO because it controls the Bosporus strait 1 - the entrance from the Black Sea to the Mediterranean. Except for that, there is the Dardanelles Straits7, which is between the Sea of Marmara and the Aegean Sea 1, the Russian fleets will have to navigate through if they want to get to the Aegean Sea en route to the Mediterranean.
-
The Bosporus or Bosphorus is a narrow, natural strait and an internationally significant waterway located in northwestern Turkey. It is one of the Turkish Straits, along with the Dardanelles. It forms part of the boundary between Europe and Asia, and separates the Black Sea and the Sea of Marmara.
-
Mustafa Kemal Atatürk (1881-1938) was a Turkish military officer, revolutionary statesman, and founder of the Republic of Turkey. He was the first president of the Republic, serving from 1923 to 1938. Atatürk is credited with transforming the Ottoman Empire into a modern and secular nation-state, and is regarded as a national hero in Turkey. ↩︎
-
Turgut Özal was the 8th President of Turkey, serving from 1989 to 1993. He was known for his economic reforms, which liberalized the Turkish economy, and for his efforts to bring peace to the region. He was a religious man and advocated for religious freedoms and tolerance. ↩︎
-
Recep Tayyip Erdoğan is a Turkish politician who has been the President of Turkey since 2014. Prior to that, he served as Prime Minister from 2003 to 2014. He is the founder and chairman of the Justice and Development Party (AKP). He is known for his conservative and authoritarian policies, which have been criticized by many. ↩︎
-
The Syrian Civil War is an ongoing armed conflict in Syria, which began in 2011 between the Ba’athist Syrian Arab Republic led by President Bashar al-Assad and various domestic and foreign forces opposing the government. The war has resulted in a humanitarian crisis and has been described as the worst humanitarian disaster of the 21st century. It has caused the displacement of millions of Syrians and has resulted in the deaths of over 500,000 people. ↩︎
-
More from wiki:Israel-Turkey relations. ↩︎
-
The Dardanelles Straits, also known as the Hellespont, is a narrow, natural waterway that separates the European and Asian sides of Turkey. It connects the Sea of Marmara to the Aegean Sea, and is also the main access from the Mediterranean to the Black Sea. Historically, it has been of great strategic importance and has been the site of numerous battles. ↩︎